
writer: Mochammad Qomaruddin
The low utilization of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) waste as the main material for rigid pavement is due to weaknesses in the bond of the existing aggregate asphalt layer.
Many researchers admit that the use of RAP for rigid pavement construction is ineffective
and inefficient. The objectives of this research are
(1) to develop a pyrolysis method for
extracting asphalt from RAP,
(2) to find chemical elements that cause a decrease in the
quality of RAP mortar,
(3) to analyze the effect of RAP pyrolysis on the mechanical
properties of mortar,
(4) to analyze the interface between aggregates with cement paste.
The novelties proposed for in this research are
(1) The extraction of asphalt through pyrolysis
(2) Mechanical properties of mortar using pyrolysis aggregate on compressive strength, flexural strength and failure pattern.
The research method used is experimental
in the chemistry laboratory and in the construction materials laboratory. The test methods used in the laboratory are: SEM, EDX, FTIR, asphalt content extraction test, mortar compressive strength test and mortar flexural tensile strength test. The results obtained were
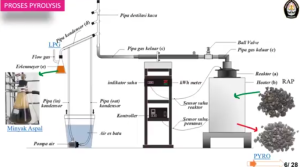 (1) Extraction of RAP aggregate asphalt using the pyrolysis process was 0.95% lower than asphalt extraction using the centrifugal method.
(1) Extraction of RAP aggregate asphalt using the pyrolysis process was 0.95% lower than asphalt extraction using the centrifugal method.
(2) The chemical elements of asphalt attached to the RAP aggregate are hydrocarbons and sulfur, where a thin layer of RAP asphalt is the cause of a decrease in the quality of the mortar. In PYRO, there exists sulfur which led the mortar produced is lower compared to mortar of NA, which caused by the loss of hydrocarbon from pyrolysis process
(3) The ability of PYRO mortar to increase compressive strength by 23% and tensile strength by 20% compared to RAP mortar.
The PYRO mortar can be used as rigid pavement which fulfill the requirement of SNI 8457 (2017) with flexural strength of 3.5 to 4.1 MPa on 28 days which resulted in 5.86 MPa (4) The thin asphalt layer of RAP aggregate has micro cracks at the interface of the RAP aggregate and cement paste. The relationship between compressive strength and flexural strength obtains a relationship coefficient value of ft c for mortar aged 28 days for each aggregate NA 1.28; RAP 0.97 and PYRO 1.02. The failure pattern of the mortar cubes occurs crushing and the failure pattern of the blocks occurs with broken cracks located in the middle of the span due to moments with the surface area of loose aggregate due to ITZ being RAP of 15.44%.
